Key takeaways
In any business, managing transactions manually can lead to errors, slower service, and unhappy customers. A point-of-sale (POS) system is a valuable and practical tool to avoid the drawbacks of manual processes. POS systems speed up transactions and reduce the risks of human error. They also streamline business operations by making inventory management easier, providing quick access to business data, and integrating with your other business systems.
What is a POS system?
A basic POS system is a combination of hardware and software that allows businesses to accept payments efficiently. Beyond just processing payments, a POS system may also complete or help coordinate key business functions like inventory management, customer relationship management (CRM), and sales reporting.
In essence, a POS system is the nerve center of any brick-and-mortar business, and there are different types of POS systems to fit different business needs.
Key components of a POS system
Several essential components make up a POS system. These components work together to facilitate seamless transactions:
Hardware components
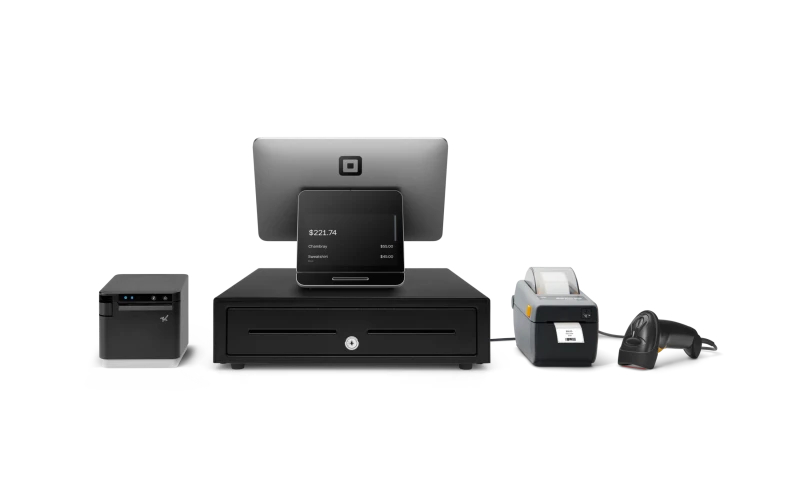

- POS terminal: The POS terminal is the main device that processes sales transactions. This device may be a computer, a tablet, a mobile phone, or a specialized POS terminal. It runs the POS software and connects to other hardware components.
- Card reader: A device that accepts payments by reading card information by swiping, tapping, or dipping the card into the device. Some POS terminals may also function as card readers, and some POS software can use mobile phones to function as card readers.
- Receipt printer: Provides printed receipts for customers, confirming their purchase details. Many newer systems also offer digital receipts via email or SMS.
- Barcode scanner: Helps quickly input product information into the system by scanning barcodes, speeding up the checkout process and reducing errors.
- Cash drawer: Securely stores cash transactions. It connects to the POS terminal and opens automatically when a cash payment is processed.
Although some POS set-ups have these components as separate devices, many providers also offer all-in-one terminals that function as a card reader, a receipt printer, and a barcode scanner.
Software components
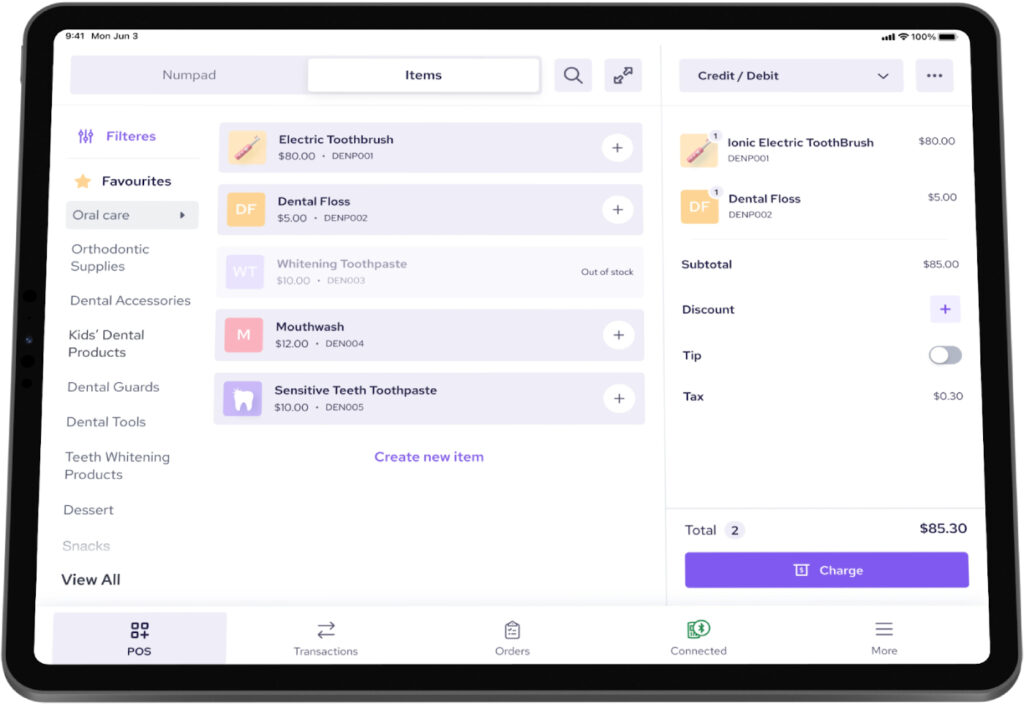
- POS software: The application that runs the entire POS system. It can be installed locally on the device/terminal or cloud-based.
- Sales reporting: Provides detailed reports on sales trends, employee performance, and other key metrics. Most POS systems have reporting capabilities, only differing in the complexity and level of insight the reports can provide. This can range from basic daily sales reports and product performance to more complex summaries.
- Inventory management: Not all POS systems have inventory management capabilities. However, those that do can typically track stock levels, update quantities as sales are made, and generate low-stock alerts.
- Customer relationship management (CRM): Stores customer data, including purchase history, preferences, and contact information, enabling personalized service and targeted marketing efforts.
How does a POS system work?
A POS system makes sure that a sales transaction proceeds smoothly from start to finish. Here’s how it typically works:
- Customer initiates the purchase: The process starts when a customer decides to purchase a product or service. The cashier or store employee scans the items using a barcode scanner or manually enters the product details into the POS system.
- Total amount calculated: The POS system automatically calculates the total amount due, including any applicable taxes or discounts.
- Payment is processed: Once the total is calculated, the customer may choose the payment method they’d like to use from the options accepted by the POS system. Some common payment methods are cash, credit or debit card, and mobile wallet.
- Transaction is completed: After the payment is approved, the POS system finalizes the sale. If the POS system has inventory management, the inventory is updated as well. A receipt may also be printed out or sent digitally to your customers.
- Transaction is recorded: The POS system records all transaction details, storing them in the system’s database, which may be accessed and analyzed at any time. This information is then available for generating sales reports, tracking employee performance, processing future returns or refunds, and providing insights into customer behavior.
Benefits of a POS system
Using a POS system offers numerous advantages that extend beyond basic transaction processing. These benefits can significantly enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and overall management of your business operations:
- Improved efficiency: A POS system speeds up sales processes by automating tasks like price calculation, inventory updates, and payment processing. This reduces customer wait times and frees staff to focus on other important aspects of the business.
- Decreased errors: Automating data entry and calculations will help improve accuracy and lessen human errors that often happen with manual processes.
- Easier inventory management: Even a POS system’s most basic inventory management feature can significantly improve inventory efficiency and accuracy.
- Enhanced business insights: POS data helps provide quick access to reports and analytics, provides better insights into your business, and helps you make more informed decisions.
- Better customer experience: Speeding up transactions, reducing errors, and offering features like digital receipts and loyalty programs will help improve the overall customer experience.
- More streamlined operations: Many POS systems can integrate seamlessly with other business tools, such as accounting software, ecommerce platforms, and CRM systems. This integration streamlines operations and ensures all your business systems work cohesively.
POS software features
Software is the backbone of any POS system. While features can vary depending on the specific software and industry, here are some of the most common POS software features:
- Sales and transaction management: At its core, POS software handles sales transactions efficiently, processing payments, applying discounts, calculating taxes, and generating receipts. It ensures that every sale is accurately recorded and streamlined.
- Payment processing: POS software supports various payment methods, including credit/debit cards, mobile payments, gift cards, and more. Some systems also allow for split payments, installments, and deposits.
- Ecommerce integration: For businesses with an online presence, POS software can integrate with ecommerce platforms to manage online orders and accept online payments.
- Inventory management: POS software often includes robust inventory management features for tracking stock levels in real-time, setting reorder alerts, and managing supplier information. This helps prevent stockouts and overstocking.
- Customer relationship management (CRM): Many POS systems integrate CRM tools to manage customer data, track purchase history, and implement loyalty programs. These features help businesses personalize the customer experience, promote repeat business, and improve customer satisfaction.
- Employee management: POS software often includes features for managing employee schedules, tracking work hours, and monitoring performance. POS software also typically allows businesses to assign different access levels to employees, ensuring that sensitive data is protected while allowing staff to perform their duties efficiently.
- Sales reporting and analytics: Advanced POS software provides detailed reporting and analytics on various aspects of your business, including sales trends, top-performing products, and employee performance. These insights enable you to make data-driven decisions that can boost profitability and operational efficiency.
- Multi-channel integration: Modern POS software can integrate with other sales channels, such as online stores or mobile apps. This ensures that your inventory, sales data, and customer information are synchronized across all platforms.
- Mobile POS capabilities: Many POS software solutions offer mobile POS capabilities that allow you to accept payments and manage sales from a smartphone or tablet. This is particularly useful for businesses that operate in multiple locations, offer on-the-go services, want to take payments on the sales floor, or sell at events.
- Security features: POS software often includes built-in security measures, such as encryption, user authentication, and fraud detection, to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with industry standards, such as PCI DSS.
How to choose a POS system for your business
Selecting the right POS system for your business is a critical decision that can significantly impact your operations, customer experience, and profitability. Here are key considerations to guide you in choosing the best POS system for your business:
1. Assess your business needs
Start by evaluating your business’s specific needs. Consider factors such as the size of your operation, your industry, and the complexity of your sales process. For example, a retail store might prioritize inventory management features, while a restaurant might need robust table management and quick service capabilities.
2. Determine your budget
Establish a budget that includes the POS system’s initial cost and ongoing expenses like monthly fees, transaction fees, and add-on features. Understanding your budget constraints will help narrow your options and ensure you choose a system that provides good value without overspending.
3. Consider ease of use
The POS system should be user-friendly, with an intuitive interface that’s easy for you and your staff to learn and use. An overly complex system can slow down operations and lead to frustration. Look for a system that offers a clean, straightforward design and has adequate help and training resources.
4. Check for essential features
Make a list of your business’s must-have features, such as inventory management, sales reporting, CRM, and multi-channel integration. Ensure that the POS system you choose offers these features and aligns with your business needs and goals.
5. Evaluate flexibility and scalability
As your business grows, your POS system should be able to scale with you. Choose a system that offers flexibility, such as adding new locations, integrating with additional software, or handling increased transaction volume. This ensures that your POS system can support your business as it expands.
6. Ensure security and compliance
Security is critical when choosing a POS system. To protect customer payment data and personal information, ensure that the system complies with industry standards, such as PCI-DSS and GDPR. Additionally, look for features like encryption, user authentication, and fraud detection to safeguard your business.
7. Research customer support
Reliable customer support is essential for addressing any issues that may arise with your POS system. Check the availability and quality of customer support services, including hours of operation, response times, and support channels (phone, email, chat). A system with strong customer support can minimize downtime and ensure that your business continues to run smoothly and you have access to support if anything goes wrong.
Best practices for using a POS system
To maximize the effectiveness of your POS system and ensure smooth operations, it’s crucial to follow these best practices:
- Regularly update software and hardware: Ensure that both POS software and hardware are up-to-date with the latest features and security patches to maintain optimal performance and protect against vulnerabilities.
- Train staff thoroughly: Provide comprehensive training for all employees on how to use the POS system efficiently. Proper training minimizes errors and maximizes the system’s capabilities.
- Back up data routinely: Implement a routine backup process for all data stored in the POS system to prevent loss in case of system failures or other issues.
- Monitor and analyze reports: Review sales reports, inventory levels, and customer data to make informed business decisions and identify areas for improvement.
- Integrate with other systems: Integrate the POS system with other business tools, such as accounting software and CRM systems, to streamline operations and ensure consistency across platforms.
- Implement strong security measures: Use encryption, strong passwords, and access controls to safeguard sensitive information and comply with industry security standards.
- Review system performance: Evaluate the POS system’s performance periodically to ensure it meets your business needs and consider upgrades or changes if necessary.
Future trends in POS systems
The POS landscape has already seen significant shifts due to technological advancements and changing consumer behaviors. Cloud-based POS systems and mobile POS solutions are becoming the standard as they offer flexibility and allow businesses to process payments on the go. The mPOS market value in 2023 is $34.72 billion, while the cloud POS market is growing at a rate of almost 25%.
Additionally, there is a growing demand for integrated omnichannel experiences, where POS systems synchronize data and functionality across online, in-store, and mobile platforms. Around 71% of merchants consider integration with other systems as a top functionality they look for in their POS.
Contactless payments are also widely adopted, driven by the need for faster and more secure transactions. These developments have set the foundation for the possible next wave of innovation in POS systems.
AI-driven personalization and automation
The future of POS systems will increasingly rely on artificial intelligence (AI) to deliver personalized customer experiences and automate routine tasks. AI is a top priority for 57% of businesses when choosing POS systems.
AI will enable POS systems to analyze vast amounts of customer data, predict preferences, and offer personalized recommendations. This will enhance customer satisfaction and increase sales and loyalty.
AI-driven chatbots will automate tasks such as inventory management, reordering, and even customer support, further streamlining business operations.
Advanced data analytics and predictive insights
According to a Grand View Research report, the global advanced analytics market will grow at a CAGR of 21.1% from 2022 to 2030. While basic reporting is now standard, future POS systems will offer more advanced data analytics, providing businesses with predictive insights. These systems will analyze historical sales data, market trends, and customer behavior to forecast demand, optimize inventory, and even predict staffing needs. This level of foresight will allow businesses to make proactive decisions.
Biometric and blockchain security enhancements
Security will remain a top priority. To secure transactions, future POS systems will incorporate cutting-edge technologies like biometric authentication (e.g., fingerprint or facial recognition) and blockchain. The biometric market is expected to grow 19.7% from 2020 to 2025, while the global blockchain technology market is expected to grow roughly 68% from 2022 to 2030.
These technologies provide an additional layer of protection against fraud and data breaches, ensuring that customer information is kept safe.
Self-service and autonomous checkout
The self-service kiosk market is expected to grow by 5.6% from 2024 to 2036. This trend will continue to grow, with future POS systems incorporating more advanced autonomous checkout solutions. Technologies such as computer vision and AI will allow customers to check out by simply placing items in their cart and walking out. This will reduce wait times and enhance the shopping experience, particularly in high-traffic retail environments.
Voice-activated POS systems
The global voice recognition tech market is expected to reach $50 billion by 2029. With the rise of voice-activated technology, future POS systems may incorporate voice commands for tasks such as ringing up sales, managing inventory, or generating reports. This hands-free functionality could speed up operations and make POS systems more accessible for businesses with busy environments or those looking to reduce physical contact points.





