Key takeaways
What is virtual reality training?
Virtual reality (VR) training uses specialized technology — like headsets, surround sound, and gaming controllers — to teach trainees new skills in a completely digital environment. The training typically mimics real-world scenarios employees could encounter in their jobs so they can learn and practice new skills without real-world consequences.
Although VR training is a type of hands-on training, it differs from on-the-job training since it takes place in a digital environment, and employees do not produce any actual deliverables. VR training is also distinct from game-based learning.
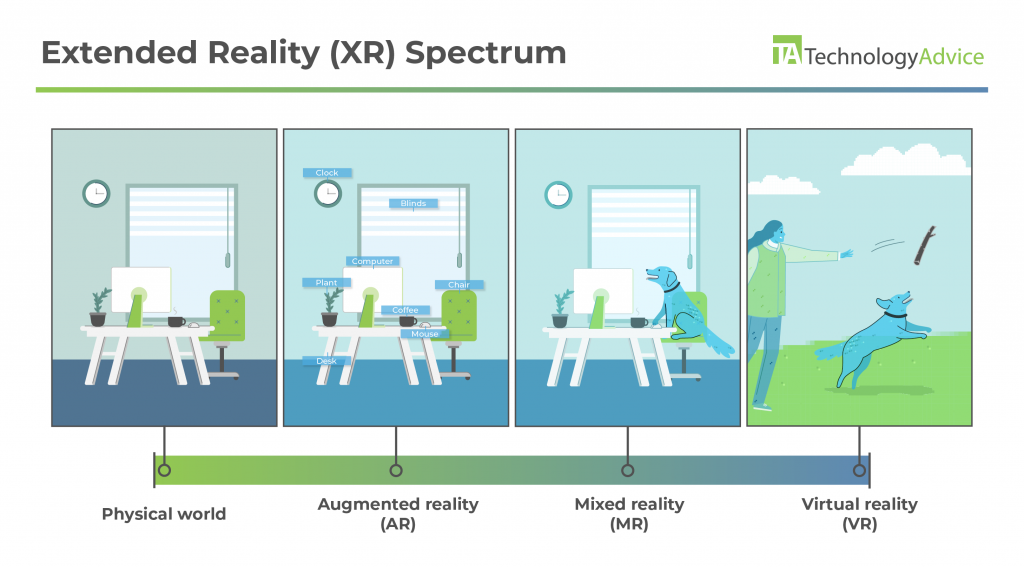
Virtual reality training falls within the broader spectrum of extended reality (XR) technology and training techniques. Below are the different shades of the XR spectrum or virtuality continuum:
Because virtual reality is the most immersive, you can train employees on subjects or scenarios that may be too impractical, unsafe, or expensive in the real world. Plus, with subject matter experts or senior experts in your company creating the scenarios and scripts for the VR experiences, your employees are more likely to form memories associated with the training and retain them for longer.
Examples of VR training
While most organizations can benefit from it, some examples of areas where VR can make the most impact include technical skills; health, safety, and security; leadership and communication; diversity, equity, and inclusion; and employee wellness.
Technical skills
Because VR training is entirely digital, traditionally dangerous industries can use VR to teach skills that would be risky to practice without precision in real life. They include the technical competencies needed in industries like:
VR training has been trending in healthcare for years, allowing students to practice surgeries, test treatments, and even learn bedside manners.
For workers in high-risk industries like construction, manufacturing, and agriculture, VR helps them learn their roles quickly and become acquainted with the equipment they use daily. SkillsVR, for example, can customize VR training courses based on the specific hard skills your employees need.
Check out an example of SkillsVR’s technical skills VR training for kiwi fruit pruning in New Zealand.
Heath, safety, and security
VR allows employees to test their health, safety, and security knowledge by exposing them to dangerous situations. In these virtual scenarios, employees can identify hazards and take steps to prevent or reduce injury to themselves, coworkers, or customers. Employees can even practice mandated compliance training for their industry, such as using personal protective equipment (PPE) and fire prevention by OSHA.
Even if you’re a low-risk company, you can use VR to simulate security issues employees may face in an office environment, such as phishing scams or other threats to the company’s physical or intellectual property. HR professionals, in particular, can use VR to learn how to investigate and document workplace incidents when they happen properly.
See how you can conduct your ladder safety training with VR vendor PIXO:
Leadership and communication
Leadership and communication are critical soft skills employees need to succeed and grow in their roles. While most communication or leadership training focuses on theory, like in self-paced eLearning courses, VR allows employees to put theory into practice by interacting with colleagues, direct reports, or customers in real-life scenarios.
Emma Ridderstad, co-founder and VP of Warpin Reality, notes the particular success that Sweden’s postal system, PostNord, had with Warpin’s VR training. Beyond developing skills like package sorting, Warpin placed postal trainees in simulated environments to navigate difficult conversations for leadership and communication practice.
PostNord reports VR training is more effective and faster than the online learning courses they used before:
Diversity, equity, and inclusion
In recent years, VR training has added a creative approach to diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) training. Because of its ability to immerse people in real-life situations, VR can place employees in scenarios where they experience microaggressions or other biases firsthand. The goal is to build awareness and allyship for diverse groups in the workplace.
Samantha Karlin, founder and DEI trainer at Empower Global, explains how she partnered with VR training vendor Equal Reality to conduct DEI training for her clients. In particular, she notes the effectiveness this immersive and often emotional training can have on senior leadership groups, especially for implementing progressive policy changes.
Explore Equal Reality’s VR training below:
Employee wellness
Wellbeing training teaches individuals how to manage their physical, mental, and emotional health. In the workplace, wellness training can show employees how to recover from emotionally charged conversations, manage stress, or form better working habits for increased productivity.
Ridderstad is particularly excited with VR’s capabilities in this space, explaining how psychologists use VR to help patients confront phobias, including social ones, with their therapist guiding them. Warpin’s training platform, Xelevate, even includes a wellness module that transports trainees to Sweden’s UNESCO World Heritage site, Höga Kusten. There, employees can stretch, meditate, and regain composure, especially after stressful situations.
Check out how it’s done in the video below:
Benefits of VR training
If implemented correctly, VR training is a highly effective form of training to add to your company’s learning and development programs, with the following benefits:
Improves knowledge retention
According to 2015 data from Miami Children’s Health System, employees retain as much as 80% of what they learned in a VR session a year after the training — compared to only 20% retention after a week using traditional methods.
More recent data from a 2020 PwC study indicates employees were more confident and connected with the content in VR training versus classroom training. This, plus the engaging nature of VR, can help learners overcome the Ebbinghaus Forgetting Curve and retain meaningful information for longer.
Accelerates skill mastery
According to PwC’s 2020 VR Soft Skills Training Efficacy Study, employees are four times faster to train using VR than in the classroom. As a result, VR accelerates employee proficiency in a skill, subject, or topic to produce a more knowledgeable workforce.
This can be especially useful in succession planning or upskilling and reskilling employees to fill positions when others leave. VR can make getting these employees ready for a role quicker and reduce any loss of productivity.
Boosts situational confidence
PwC’s 2020 study also showed employees were 275% more confident in applying the skills they learned from VR training — a 40% improvement over the classroom and a 35% improvement over eLearning. Employees are more likely to practice what they learned in a VR simulation, which reduces the need for trainers to walk through procedures with employees and causes fewer interruptions to company workflows.
Increases employee engagement
Employees are entirely immersed in a virtual environment, meaning they cannot easily walk away from what they are learning, and distraction is difficult. PwC’s 2020 study even confirmed trainees are four times more focused during VR training than eLearners.
Although VR is not a video game, the novelty of wearing VR headsets, using controllers, and navigating through illustrated environments can get employees excited about learning. Karlin notes how the mere mention of VR training can pique employees’ interest, even if it is on a dull topic or skill.
Lowers accident risk
Using VR training to master skills that can be dangerous to practice in real life reduces the chance of harm to peers, managers, customers, or learners. Combined with improved knowledge retention, VR makes employees more likely to respond appropriately to injuries, accidents, or other security incidents in the workplace. In turn, this reduces the chance of costly mistakes.
Accommodates learner preferences
VR training satisfies most employees’ learning preferences, whether they’re visual, audio, or kinesthetic learners, by using immersive graphics, surround sound, and interactive elements in the virtual environment.
Moreover, depending on the training, VR accommodates blended learning, self-taught, or full-scale group sessions with a trainer and post-lesson debrief. As a result, employees can learn and resonate with the subject matter in a way that makes sense for them.
Challenges of VR training
Despite the benefits of VR training, it poses a lot of challenges that may be difficult for small organizations to overcome, such as:
Cost
The sheer upfront costs of VR training might be too high for some companies to afford. Depending on the type of VR headset and the manufacturer, prices can range anywhere from $300 to over $1,000 per headset alone — and this typically doesn’t include auxiliary equipment such as controllers, AV equipment, or monitors.
Content is an additional expense, with customized VR training programs easily exceeding $50,000. Plus, while some VR training can integrate with your learning management system (LMS) to assign, manage, and track content KPIs, others may need a separate extended reality system (XRS). Like LMSs, XRSs incur an additional annual or monthly subscription fee.
Therefore, the total upfront costs of VR include the following:
Depending on your employee count, training cadences, and content depth, your VR training could cost well over $100,000. Therefore, VR training is usually not the most practical option for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) just developing their training content.
However, PwC’s 2020 VR Soft Skills Training Efficacy Study indicates that VR training is cost-effective compared to other learning methods if done at a large enough scale — with at least 1,950 learners.
At that level, companies will have already purchased the necessary equipment and tailored their VR training content for reuse as new employees start. Meanwhile, LMS subscription costs to cover that employee headcount may not be worth continuing, especially considering the speed and retention of training with VR.
What if I’m a small or medium-sized business? While full-scale VR training might not be the best choice if you have fewer than 1,000 employees, plenty of free and low-cost eLearning training options are available. You can learn about some of these options in our roundup of the best learning management systems (LMS) for small businesses.
Scalability
According to Karlin, the logistical nightmare of VR training can be a lot for organizations to overcome. Headsets, for example, are “not scalable” since some manufacturers limit the number you can buy at once. Also, renting headsets can be challenging if you need training on a routine basis rather than just a one-off event.
Even with the proper equipment available, you’ll need to be mindful of the physical space required for VR training and the number of trainers to assist in the sessions. Trainers must be knowledgeable of the content, host debriefs after the training, and be able to provide technical assistance to trainees throughout.
Purchasing and sending headsets and other equipment to employees can be impractical if your organization has a distributed or remote workforce. Even with device management tools, you must also account for training in various languages and orchestrating training sessions in multiple time zones.
Therefore, as your company scales, VR training becomes more challenging to manage and maintain consistency across multiple locations and departments than eLearning methods.
Executive buy-in
Considering virtual reality’s cost and scalability, convincing your executive team to invest in this type of training can be an uphill battle. Your HR or L&D teams will need to adequately prepare data to show the effectiveness and cost of your current training methods over time and compare them to the predicted return on investment (ROI) of VR training.
Despite VR’s stellar retention and training rates, it might be difficult to convince executives in traditionally high-turnover industries, like restaurants and retail, that VR will make the most impact. In these situations, investing in software with gamified elements might be more practical to keep employees engaged.
Diversity, equity, and inclusion
VR allows employers to make considerable strides in training their employees on DEI by making it more impactful and personable. However, DEI VR training can also easily perpetuate stereotypes or create employee tensions.
For example, a current trend in VR for DEI training is placing white male employees into black female virtual avatars to experience various forms of discrimination and microaggressions firsthand. While the intent is to build empathy and understanding of what black women could and often face, it ignores how putting white people in the bodies of people of color can invoke the painful and racist history of blackface in the U.S.
That does not mean DEI VR training cannot be transformative. For example, both Ridderstad and Karlin note VR’s particular use in exposing gender stereotypes and helping women advance in traditionally male-dominated industries.
So, consider your audience before using VR for DEI training. You can leverage surveying software, like Culture Amp, to determine the technique and focus of your VR DEI training while gauging employee interest or any reservations before implementation.
Check out our video overview of Culture Amp below:
Accessibility
VR training presents many accessibility challenges, including:
Despite this, Karlin argues that VR can make interacting with the world more accessible for individuals with moderate vision or hearing loss.
VR headsets can fill employees’ entire field of vision, magnify important areas, and use bold contrast, which can be especially useful for employees with low vision. Surround sound can also make it easier for hard-of-hearing employees to pick up on sounds they would otherwise not hear in the physical world and adjust the volume as necessary. As Karlin explains, VR allows them to connect to their training by customizing their sensory experiences.
However, not all headsets and software are created equal, so finding these can be a difficult challenge to consider as you develop your VR training.
VR training requirements
Unlike traditional or eLearning methods, VR training involves several technical and logistical requirements to successfully implement, including:
The future of virtual reality training and technology
Virtual reality may not be a practical idea for every organization, but the technology continues to evolve. Considering the speed and knowledge retention of VR training for employees compared to other training methods, corporations that use it will soon have a significant advantage over those that don’t.
More importantly, VR training helps employees connect emotionally to their learning. As Karlin explains, “Feeling is the trigger of empathy. And empathy is the trigger of action. [VR training prompts] not just understanding, but behavior change.”
Because of this, VR training is instrumental in developing both the technical skills for employees to succeed in their roles plus the empathy to connect, collaborate, and appreciate their coworkers. So, as more vendors continue to innovate and make VR more affordable and scalable, the possibilities of what it can do for your company’s productivity and innovation are, virtually, endless.
Want to learn more about how technology can up your company’s learning and development programs? Check out our Learning Management System Software Guide for a list of eLearning platforms.





