Key takeaways
A hosted Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) system is another way to make and receive phone calls. The difference between a VoIP phone call and a traditional phone or Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS) call used in residential homes or business offices is VoIP uses the Internet, and POTS uses a twisted pair of copper wires, an analog-based phone line. This article explains everything you need to know about a VoIP system before you start doing research on VoIP systems for your business.
What is a hosted VoIP?
A hosted VoIP system is a telephone service that uses the Internet to make and receive calls. The service provider hosts the VoIP equipment at a service provider’s data center. The VoIP service provider owns and maintains the suite of VoIP equipment. Hosted VoIP is a cloud-based phone system that does not require on-premises equipment.
Looking for the latest in VoIP software? Check out our comprehensive VoIP Software Buyer’s Guide.
How do host VoIP systems work?
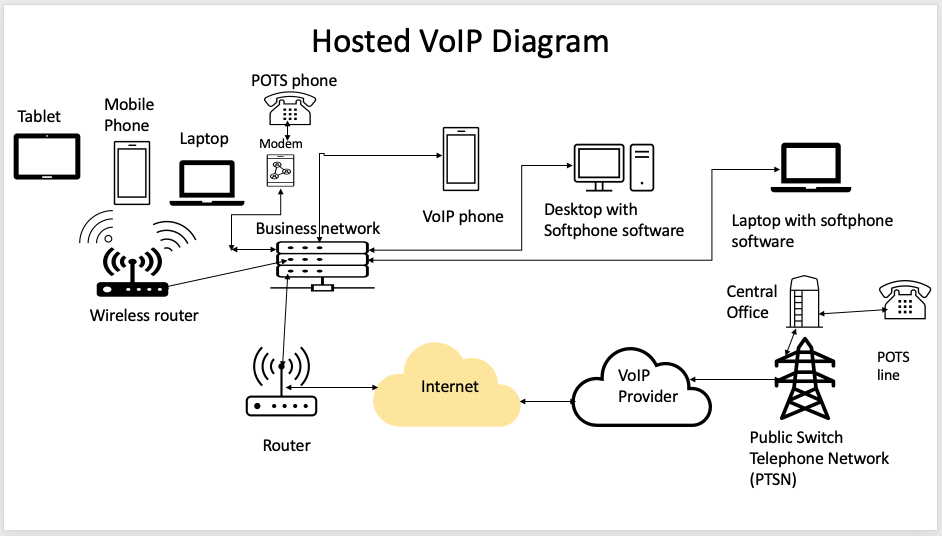
When a user makes a VoIP call, the call goes to an office router. If the call is from a POTS line in the office, a modem will convert the analog signal to a digital data packet before it goes to an office router. The digital data packet contains the recipient’s IP and phone information, which serves as the destination point. Suppose the call is to another VoIP phone number. In that case, the call will travel through the internet, passing multiple routers and switches if necessary to reach the VoIP service provider’s equipment in a data center.
When the hosted VoIP service provider’s equipment receives the data packet, the data packets are reassembled in sequential order and forwarded to the recipient’s VoIP phone. The recipient’s VoIP phone converts the digital data back to analog using a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) so the caller and recipient can converse.
When a VoIP phone call dials a recipient with a POTS line, the hosted service provider will forward the VoIP call using a VoIP gateway that converts the data packets back to an analog signal. In the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN), the analog signal will traverse to the closest local Central Office (CO) that processes calls to a POTS recipient. See Figure 1.
What equipment is needed for a hosted VoIP System?
Most businesses using a hosted VoIP solution already have a network and built-in network infrastructure with switches and routers. Minimally, for a VoIP phone to work, the following equipment is needed:
- VoIP phone and ethernet cable
- Business-quality internet connection
- Router
One of the benefits of using a VoIP solution is that other digital devices in an office, such as smartphones, desktops, laptops, and tablets, can also use VoIP services. Other items commonly associated with a hosted VoIP solution in an office setting are:
- Headsets
- Softphone software
- Conference speakers
- Analog telephone adapter
How is a host VoIP system different from POTS?
The significant difference between VoIP hosting services and POTS is the transmission medium used. Voice over IP uses digital data transmitted using packet-switching technology over the internet, while POTS uses traditional circuit-switch technology that carries electrical analog over twisted copper wires. A hosted VoIP system offers advanced features like call forwarding, caller ID, voicemail, and conference calling as standard features, while POTS primarily does audio calls and will charge for additional features that come as standard options with a hosted VoIP solution. Other advanced features in a hosted VoIP solution are the following:
- Auto attendant: Calls are automatically routed to an extension without human intervention.
- Advanced call analytics: Analyzes call data in real-time and for historical purposes.
- Instant messaging: Online chat messaging in real-time.
- Find me, follow me: Allows users to receive calls at any location, and follow me lets a user answer a call at a designated number.
- Voicemail-to-email: An audio message is forwarded to a user’s email inbox.
- Video conferencing: Used to conduct online presentations or webinars.
Hosted VoIP services offer lower costs, enhanced accessibility, and better scalability than a POTS telephone system. Traditional telephone systems are more expensive, and more maintenance is involved in supporting a POTS system. Though a hosted VoIP system provides better scalability and flexibility, it heavily relies on the internet to function, and older technology commonly associated with POTS phones, like alarms and fax machines, is incompatible with VoIP technology unless additional equipment is configured to get analog devices to work in a VoIP environment.
What are the best and worst use cases for a hosted VoIP phone system?
Hosted VoIP phone systems can significantly benefit companies when applied correctly in business environments that require 24-hour operations or have employees on a hybrid work schedule. Conversely, a hosted VoIP phone system can degrade overall business performance in some business scenarios. Here are some best and worst-case scenarios when using a hosted VoIP solution.
Best cases
Sales communication
Sales personnel are constantly moving and cannot be tied to a POTS line. Sales staff significantly benefit from a hosted VoIP solution due to the mobility VoIP phone systems provide. All calls going to a VoIP phone can be answered by smartphones, tablets, laptops, desktop computers, office phones, VoIP phones, and Web browsers when the Real-Time Communication feature is enabled. Softphone is a software application installed on laptops, desktops, and tablets, allowing users to make and receive calls without additional hardware.
Client or customer communication
Hosted VoIP phone solutions allow businesses to provide customer service 24 hours a day without an employee onsite responding to customer calls. Employees can be assigned a duty page and comfortably work remotely with a good internet connection.
Customer service or support
Like customer communication, customer support can be successfully carried out remotely with a digital device that has installed softphone software to provide 24-hour support.
Read more: Best Customer Service Software
Businesses with a fleet of vehicles
Businesses that need to remain in contact with drivers can benefit from a hosted VoIP system due to the available options to communicate with drivers. Last-minute updates or a new service request in a location that a driver may already be in reduces response time versus another driver coming from a distant location. Using a hosted VoIP solution keeps your team connected on the road.
Internal business communication onsite or offsite
Hosted VoIP systems offer a variety of methods that employees can use to communicate with each other, regardless of an employee’s location. Traditional phone systems are limited in communication options, whereas hosted VoIP services provide several communication methods, including SMS messaging and video or web conferencing.
Suppose external customers or clients requiring immediate help or assistance at any point during 24 hours can benefit from using a VoIP system due to the multiple communication options. For example, a veterinary hospital offering 24-hour emergency services or a plumbing company providing 24-hour emergency plumbing services can use one of the communication options in a hosted VoIP system.
Worst cases
Digital technology continues to optimize and improve business operations, but being new doesn’t necessarily mean it can help a business improve. Here are some business examples or scenarios in which a hosted VoIP service can negatively interfere with operations or responsiveness and the solutions that VoIP service providers can use to minimize the impact.
Emergency services
A hosted VoIP system with no built-in emergency services can doom a business. For example, a delayed response can impact an assisted living facility for senior citizens if the first responders cannot immediately determine the caller’s address. Portability is one of the popular benefits of a hosted VoIP phone system, but in this case, it can hinder first responders’ responsiveness in crucial life-and-death situations. The transfer of a landline phone number that now belongs to a hosted VoIP system is not updated in the hosted service provider system, which can lead to misinformation being provided to first responders.
Today, hosted VoIP service providers are required to associate a physical address before activating VoIP services for any business. VoIP service providers are also required to do the following:
- Link a physical address to a business phone number using Enhanced 911 services (E911).
- Automatically send registered location information to the Public Safety Answering Point (PSAP) when 911 calls are made.
- Allow customers to change their home address when they relocate.
A business that operates in rural areas without business-quality internet connectivity
Any business operating in a rural area with a low-quality internet connection should not use a hosted VoIP solution. For a hosted VoIP system to effectively meet the typical business demands, a VoIP system will require 90 kbps to 156 kbps of bandwidth. A voice call requires at least 90–100 kbps for consistent quality, and multiple VoIP phones require each phone to have 100 kbps of dedicated bandwidth available. For example, a small business with six VoIP phones in an office will require 600 kbps of bandwidth.
What are the pros and cons of hosted VoIP services?
Businesses considering the purchase of a hosted VoIP solution need to understand the pros and cons in its totality before moving forward. By reviewing and understanding the pros and cons of a VoIP system, decision-makers can ask the right questions to make sure a VoIP solution meets all of their needs.
Lower costs
Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS) phone lines average between $50-$90 per month, compared to a hosted VoIP phone line, which costs between $10 and $30 a month with a subscription plan. VoIP calls are generally cheaper because they use a business’s existing internet, while PSTN phone calls use dedicated lines that charge for international calls but not local ones. For POTS phone calls, the cost depends on the distance between the caller and the recipient, the time of day, and the length of the call.
EXPERT TIP
Adding additional calling features to a POTS line will increase the cost. Many advanced features added to a POTS line come as standard features with a hosted VoIP system. Businesses with an onsite Private Branch Exchange (PBX) with different calling features can pay as much as $800 per employee. A hosted PBX is less expensive and offers many advanced features, like a hosted VoIP system. Dedicated lines, POTS calls depending on distance and time factors, and any advanced features added to a POTS line are all costs eliminated when using a hosted VoIP solution.
Flexibility and scalability enhancements
As more companies adopt a hybrid work schedule that allows employees to work remotely, a hosted VoIP solution offers the flexibility to receive or call any business digital device using the softphone application, allowing employees to respond using a tablet, laptop, or desktop.
The ability to scale up hosted VoIP services due to a seasonal spike or hire temp employees to meet a seasonal spike is easily done with a VoIP system. Hosted VoIP scalability does not involve purchasing any telephony hardware or additional dedicated lines. Scalability for a hosted VoIP system only requires adding new phone numbers and VoIP phones, if needed. Businesses can easily add new phone numbers from their online dashboard account.
Portability
Portability allows a business to keep its POTS phone numbers and transfer its existing phone numbers to the new VoIP service provider without changing phones or SIM cards as long as the phones are in the same geographic area.
Multitasking
A hosted VoIP system allows employees to send images, documents, or videos while an employee concurrently participates in a conference call. The multitasking capability of a hosted VoIP system promotes increased efficiency and improved responsiveness, allowing businesses to meet any pressing timelines better.
Enhanced security
Hosted VoIP service providers use advanced encryption and identity management technology to minimize social engineering, with cyber security staff available 24 hours a day to protect the hosted VoIP environment. A good host VoIP service provider periodically works with an organization’s IT team and the host security team to perform security audits, ensure best practices are implemented, and review the password habits of an organization. The service provider can also use automated alerts for suspicious calling behavior.
Improved voice quality
As long as a strong internet connection exists between two parties communicating, VoIP calls are very clear with no latency issues, lags, or call drops by using noise-canceling microphones and advanced audio compression that surpasses the audio reception of POTS phones.
Cons of hosted VoIP systems
With all the positives a hosted VoIP system presents, there are specific issues businesses need to know about and how to minimize any cons associated with a hosted VoIP system.
Limitation of emergency call address location
The flexibility and portability impede first responders’ ability to know the exact location when a person calls emergency services for help. Today, hosted VoIP service providers must provide a method that allows users to update address information as needed quickly, so any phone number added to a VoIP system must have an associated address. If a VoIP user calls for emergency services and is not at the address location provided in the hosted VoIP system, it can lead to first responders going to the wrong address.
Unreliable or intermittent internet connection
Hosted VoIP systems depend heavily on a reliable internet connection. If the internet connection goes down, the VoIP phone will not work, and missed calls will go straight to voicemail. Businesses interested in using a VoIP solution must address internet connectivity problems with the service provider and their options to address bad connectivity issues.
Insufficient bandwidth can impact the quality of a VoIP call, and service providers can minimize bandwidth issues by implementing a Quality of Service (QoS) feature that prioritizes specific devices, such as VoIP phones receiving bandwidth priority when a local network is saturated. VoIP service providers can automatically reroute calls to alternate lines, a landline, or a cell phone if the internet is down. Another option for hosted VoIP service providers for an unplanned outage is a backup system that can run for 24 hours.
Compatibility with analog devices like fax machines and older alarms
Businesses considering a hosted VoIP solution and still using analog devices must seek a solution from the service provider. Technology allowing businesses to use analog devices is still available, and some VoIP providers offer online fax services as a standard option. Analog devices produce signals in waves that are not compatible with digital devices.
- VoIP providers use different technology that is not compatible with an analog alarm system, and a VoIP signal may not be recognized as an alarm signal.
- Fax machines use analog tones that can be easily misinterpreted by VoIP hardware and lose synchronization.
Businesses can also use technology that converts analog signals into digital data if a VoIP provider doesn’t offer online fax services. An Analog Telephone Adapter (ATA) can convert an analog security alarm to digital data. Though fax machines may be challenging to configure and set up to work in a hosted VoIP environment, some VoIP service providers use VoIP gateways that support T.38 fax for Wide Area Networks (WANs) or T.30 fax for Local Area Networks (LANs) technology. Patton Electronics is a company that produces VoIP gateways that support T.38 and T.30 International Telecommunication Union (ITU) protocols. The other options are PandaDoc Online and eComFax, which can provide faxing capability in a hosted VoIP environment.
Network latency and jitter
The QoS option can help reduce saturation on the network by addressing latency and jitter issues. A jitter buffer temporarily stores organized voice packets for a short, predetermined time to ensure the data packets arrive in order without delay. Jitter buffers are used to improve the quality of calls.
Power supply
A hosted VoIP service provider can maintain power during an outage by using generators, Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPSes), and Power over Ethernet (PoE) switches to keep VoIP phones operational. Enabling QoS on routers gives higher priority to the VoIP data packets on the network. Power conditioners with UPSes can regulate power fluctuations that prevent crashes.
What should you look for in a host VoIP service provider?
When looking to move to a hosted VoIP solution, businesses can start with the type of subscription packages a VoIP service provider offers.
Other questions to consider are:
These are the types of questions that will help a business make the best decision for their organization.
Choosing the right VoIP solution
Each business is slightly different, but some questions, like security practices, subscription packages, and outages, apply to all businesses. A company with unique requirements not commonly used in a typical fashion can be an afterthought to a decision-maker, so it’s essential to have participation at the lowest levels of an organization to capture all requirements.





